Class HomObjectAbstract
Hierarchy (view full)
- HomObject
Index
Constructors
Properties
Methods
Constructors
constructor
- new
Hom Object(backendClient, hostDescriptor, elementDescriptor, uiProperties, propertyRequestStrategy): HomObject Constructor for HomObject class.
Parameters
- backendClient: BackendClient
Reference to the backend client.
- hostDescriptor: DescriptorDTO
Descriptor describing the object.
- elementDescriptor: null | DescriptorDTO
- uiProperties: null | UIProperties
Optional UI properties to initialize the object with.
- propertyRequestStrategy: IHomObjectPropertyRequestStrategy
Returns HomObject
- backendClient: BackendClient
Properties
bounding
Represents the bounding box of the UI.
If the UI is a window and is minimized, the Bounding box is 0.
Remarks
Can use HomObject.updateCurrentBoundingBox to update boundingBox.
control
Represents the control type of the UI.
element
A descriptor that represents the element of the UI.
If the UI is a window, this will be null.
has
Represents whether the UI has value pattern.
Remarks
Can use HomObject.updateCurrentHasValue to update value.
host
A descriptor that represents the window to which the UI belongs, or indicates that the UI is a window itself.
id
The id of the UI.
is
Represents whether the UI has invoke pattern.
Remarks
Can use HomObject.updateCurrentIsInvokable to update isInvokable.
is
Represents whether the UI has scroll pattern.
Remarks
Can use HomObject.updateCurrentIsScrollable to update isScrollable.
is
Represents whether the UI is selected.
key
Represents the key of a UI element. The key is unique.
name
Represents the name of the UI
Remarks
Can use HomObject.updateCurrentName to update name.
scrollable
Represents the scrollable view of the UI.
Remarks
If the UI has scroll pattern, can use HomObject.updateCurrentScrollableView to update the scrollable view. Otherwise, scrollableView is null.
toggle
Represents the toggle state of the UI.
value
Represents the value of the UI.
Remarks
If the UI has value pattern, can using HomObject.updateCurrentValue to update the value. Otherwise, value is null.
Methods
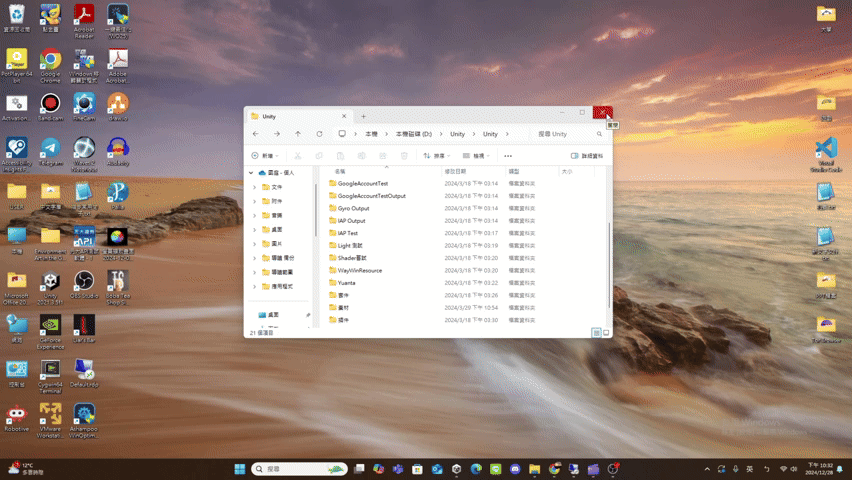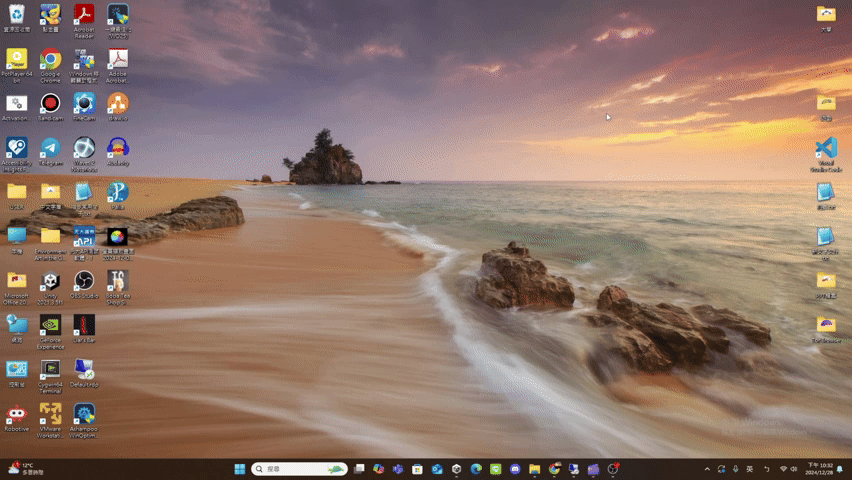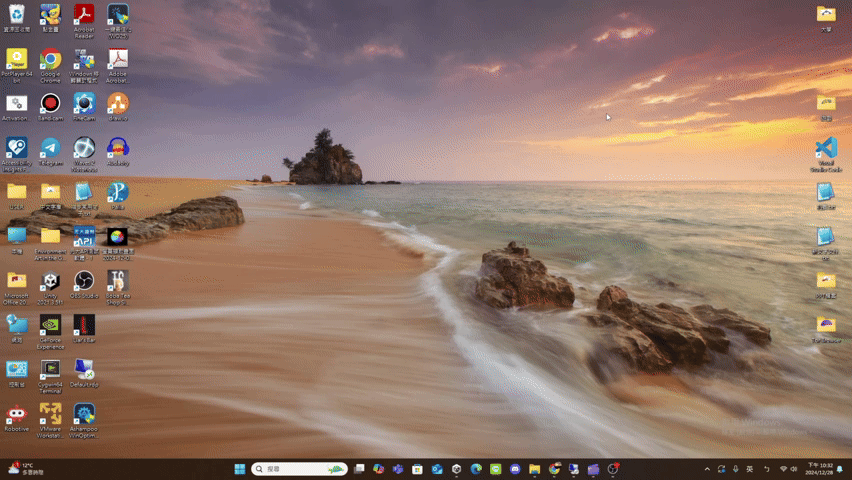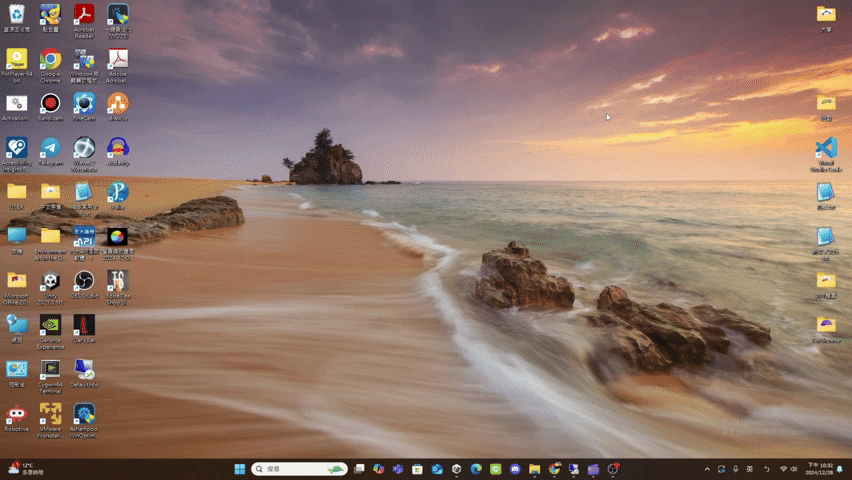
close
collapse
expand
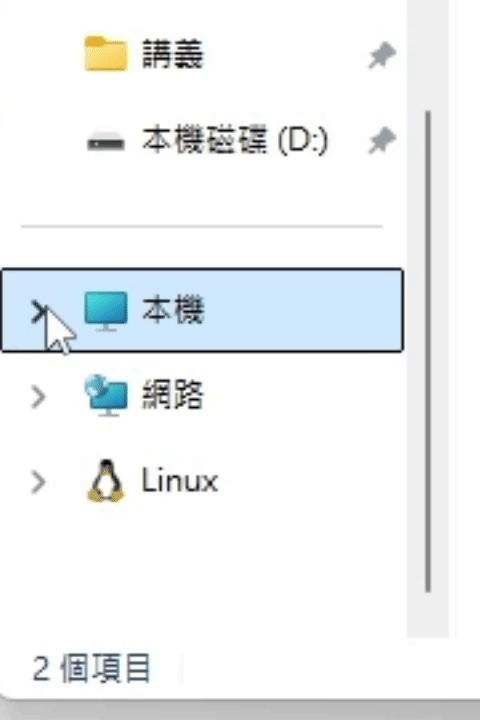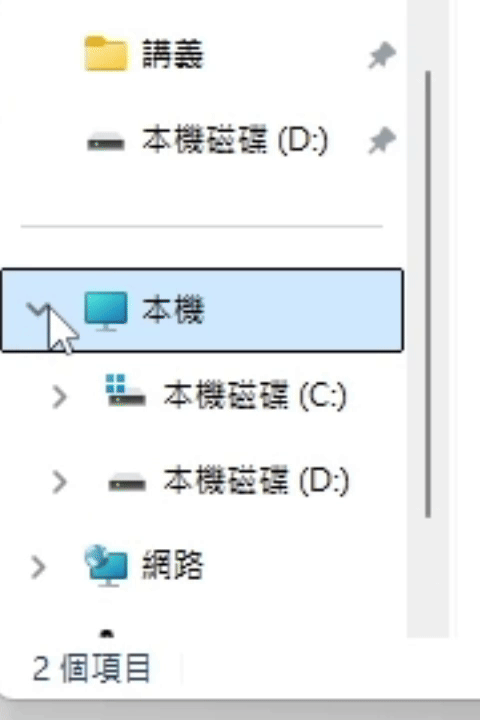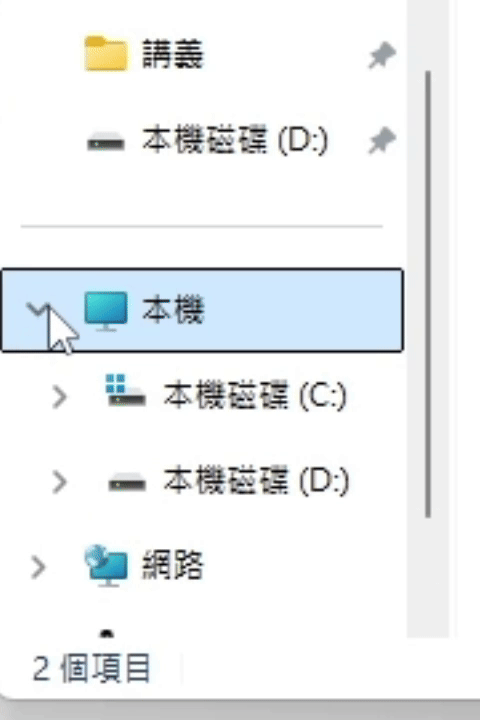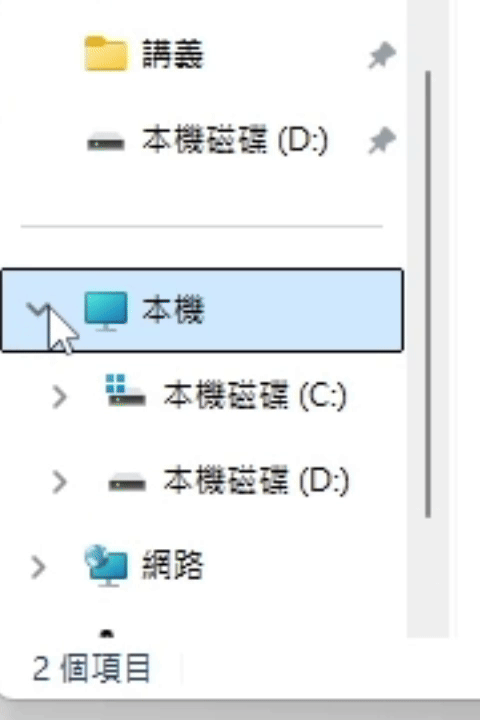
- expand(): Promise<void>
If the UI has ExpandCollapse pattern, expand the UI.
(ExpandCollapse pattern related functions are not provided yet.)Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the ExpandCollapse pattern.
Remarks
The UI result after calling expand() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
focus
get
- get
Audio Buffer(callback): Promise<void> Retrieves the audio buffer.
Parameters
- callback: ((data) => void)
The callback function to handle the audio buffer data.
- (data): void
Parameters
- data: Buffer
Returns void
Returns Promise<void>
A promise that resolves when the audio buffer is retrieved.
// Before using setValue(), must first update updateCurrentHasValue() to confirm whether there is a value pattern
await homObject.getAudioBuffer((data: Buffer) => {
console.log('Received audio buffer:', data);
});- callback: ((data) => void)
get
get
get
invoke
- invoke(): Promise<void>
If the UI has invoke pattern, invoke the UI.
(can use HomObject.isInvokable to check UI supports the invoke pattern.)Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the invoke pattern.
Example
// Before using invoke(), must first update updateCurrentIsInvokable() to confirm whether there is an invoke pattern
const isInvokable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsInvokable()
if (isInvokable) {
await homObject.invoke()
}The UI result after calling invoke() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
maximize
- maximize(): Promise<void>
If the UI has window pattern, restore the window.
(Window pattern related functions are not provided yet.)Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the window pattern.
Remarks
The UI result after calling maximize() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
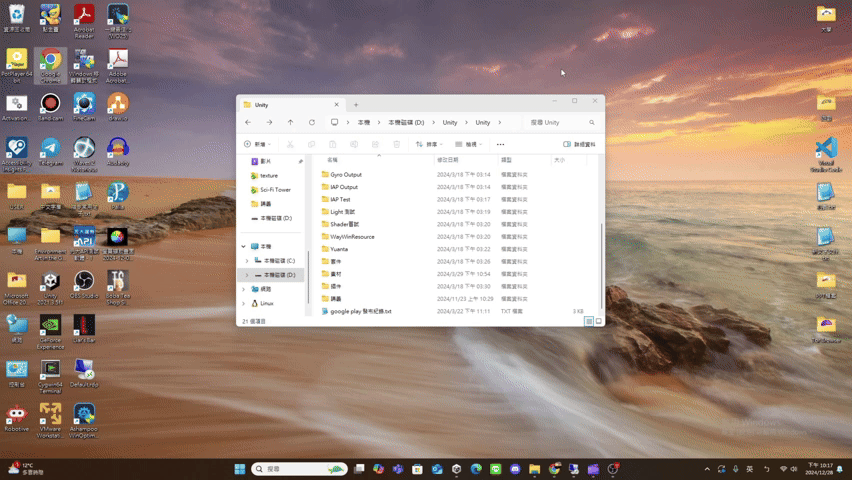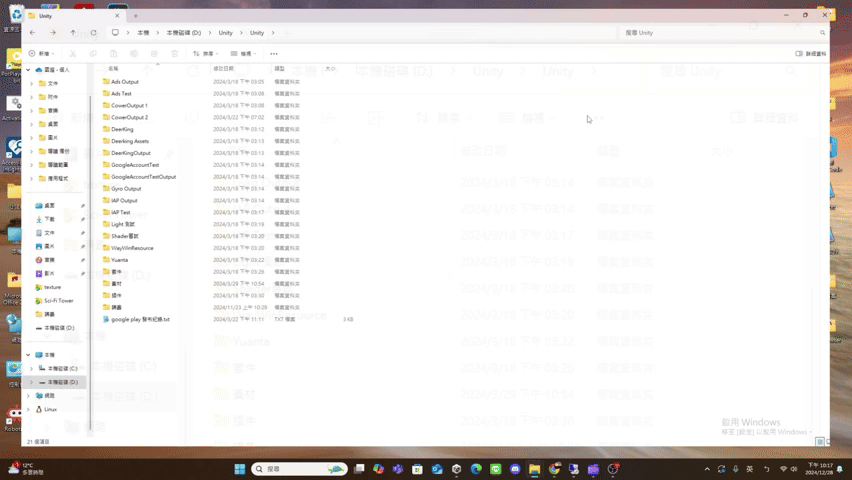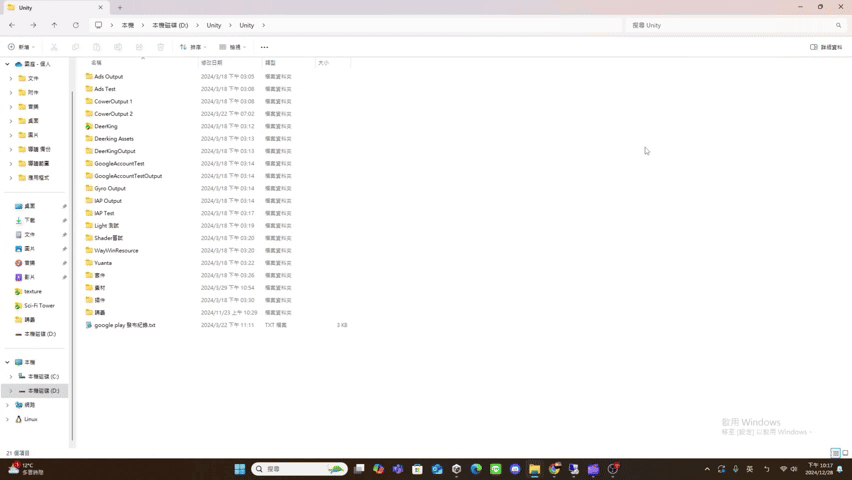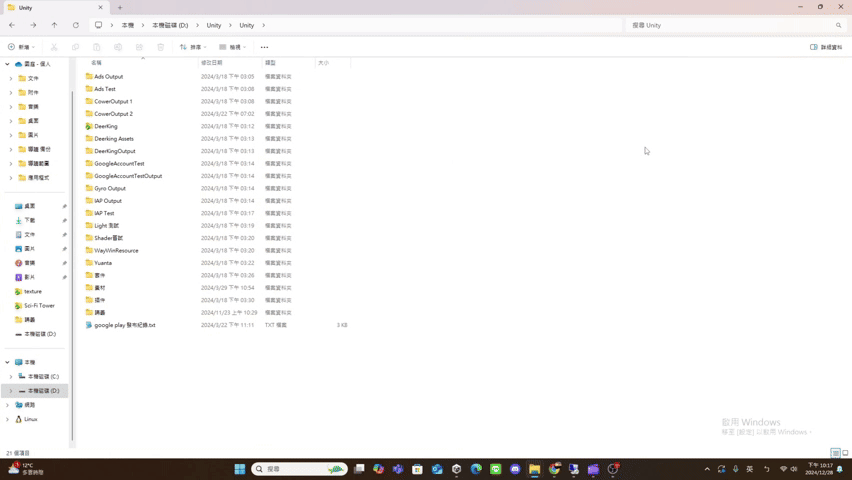
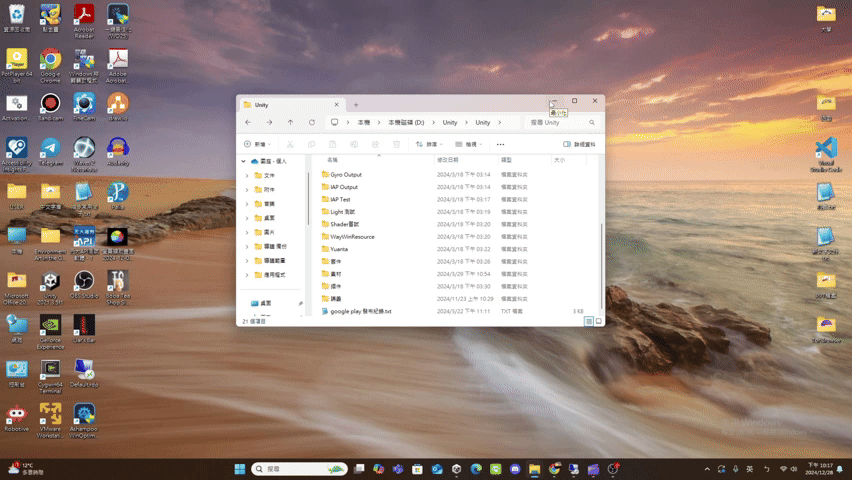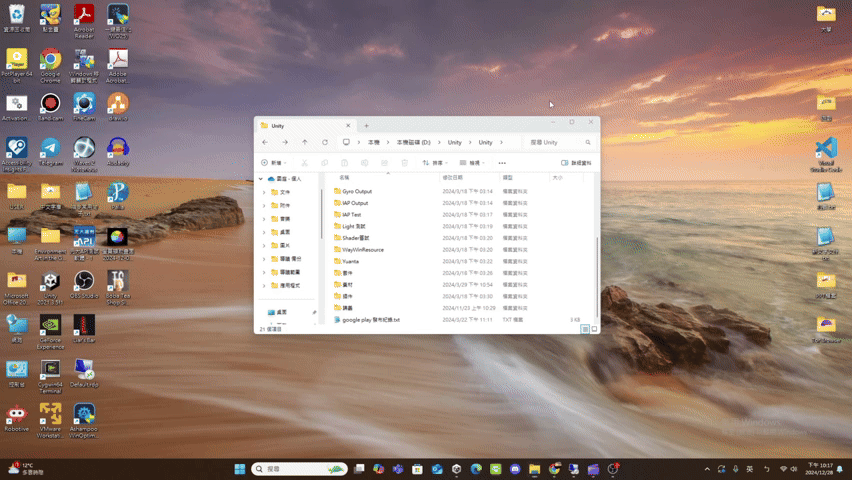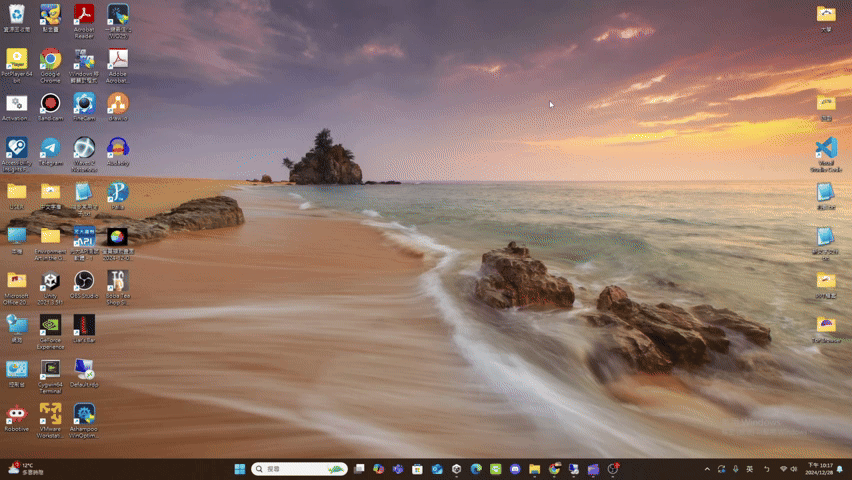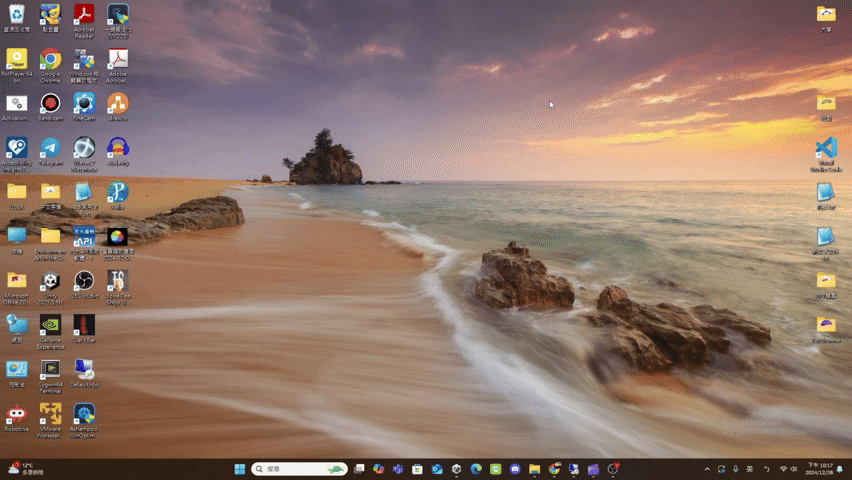
minimize
- minimize(): Promise<void>
If the UI has window pattern, minimize the window.
(Window pattern related functions are not provided yet.)Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the window pattern.
Remarks
The UI result after calling minimize() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
mouse
- mouse
Click(): Promise<void> Moves the mouse into the UI center and click.
Returns Promise<void>
Example
// Click the left mouse button into the UI center
await homObject.mouseClick()
// Click the right mouse button into the UI center
await homObject.mouseClick({ key: 'right' })- mouse
Click(option): Promise<void> Parameters
- option: MouseKeyOption
Returns Promise<void>
mouse
mouse
- mouse
Press(): Promise<void> Moves the mouse into the UI center and Hold.
Returns Promise<void>
Example
// Hold the left mouse button into the UI center
await homObject.mousePress()
// Hold the right mouse button into the UI center
// await homObject.mousePress({ key: 'right' })- mouse
Press(option): Promise<void> Parameters
- option: MouseKeyOption
Returns Promise<void>
mouse
- mouse
Release(): Promise<void> Moves the mouse into the UI center and release.
Returns Promise<void>
Example
// Hold the left mouse button into the UI center before release
await homObject.mousePress()
// Release the left mouse button into the UI center
await homObject.mouseRelease()
// Release the right mouse button into the UI center
// await homObject.mouseRelease({ key: 'right' })- mouse
Release(option): Promise<void> Parameters
- option: MouseKeyOption
Returns Promise<void>
mouse
- mouse
Scroll Down(): Promise<void> Moves the mouse into the UI center and scroll down.
Returns Promise<void>
Example
// Scroll down the mouse wheel into the UI center
await homObject.mouseScrollDown()
// Scroll down the mouse wheel into the UI center with 3 ticks
await homObject.mouseScrollDown({ tick: 3 })
// Scroll down the mouse wheel into the UI center with 120 amount
await homObject.mouseScrollDown({ amount: 120 })- mouse
Scroll Down(option): Promise<void> Parameters
- option: MouseScrollOption
Returns Promise<void>
mouse
- mouse
Scroll Up(): Promise<void> Moves the mouse into the UI center and scroll up.
Returns Promise<void>
Example
// Scroll up the mouse wheel into the UI center
await homObject.mouseScrollUp()
// Scroll up the mouse wheel into the UI center with 3 ticks
await homObject.mouseScrollUp({ tick: 3 })
// Scroll up the mouse wheel into the UI center with 120 amount
await homObject.mouseScrollUp({ amount: 120 })- mouse
Scroll Up(option): Promise<void> Parameters
- option: MouseScrollOption
Returns Promise<void>
scroll
- scroll
Horizontal(amount): Promise<void> If the UI has scroll pattern, scroll the UI horizontally.
(can use HomObject.isScrollable to check UI supports the scroll pattern.)Parameters
- amount: Amount
The amount to scroll horizontally.
Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the scroll pattern.
Remarks
// Before using scrollHorizontal(), must first update updateCurrentIsScrollable() to confirm whether there is a scroll pattern
const isScrollable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsScrollable()
if (isScrollable) {
await homObject.scrollHorizontal(Amount.LargeDecrement)
}The UI result after calling scrollHorizontal() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
- amount: Amount
scroll
- scroll
Vertical(amount): Promise<void> If the UI has scroll pattern, scroll the UI vertically.
(can use HomObject.isScrollable to check UI supports the scroll pattern.)Parameters
- amount: Amount
The amount to scroll vertically.
Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the scroll pattern.
Remarks
// Before using scrollVertical(), must first update updateCurrentIsScrollable() to confirm whether there is a scroll pattern
const isScrollable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsScrollable()
if (isScrollable) {
await homObject.scrollVertical(Amount.LargeDecrement)
}The UI result after calling scrollVertical() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
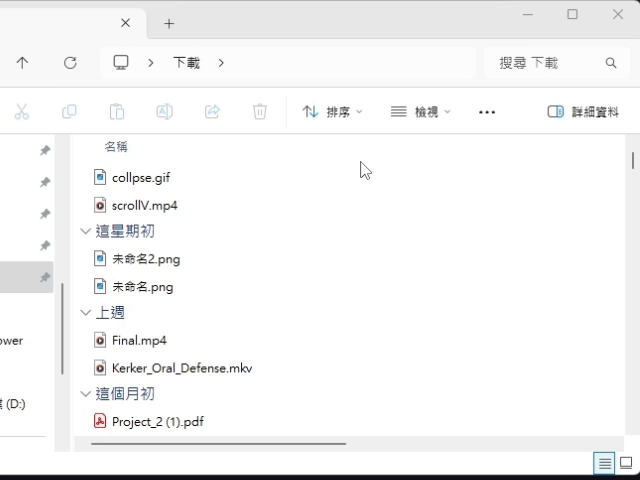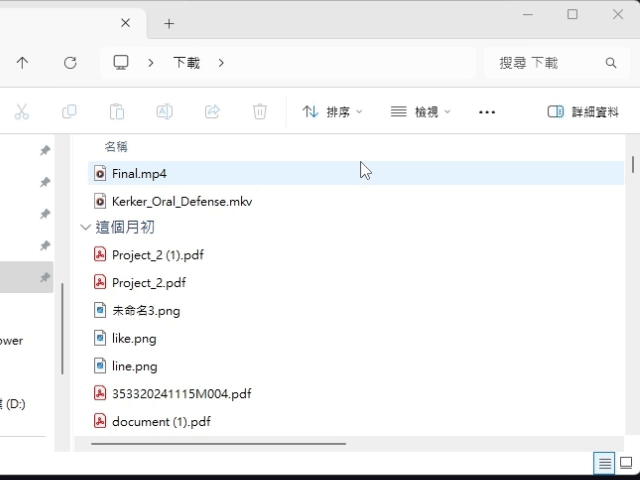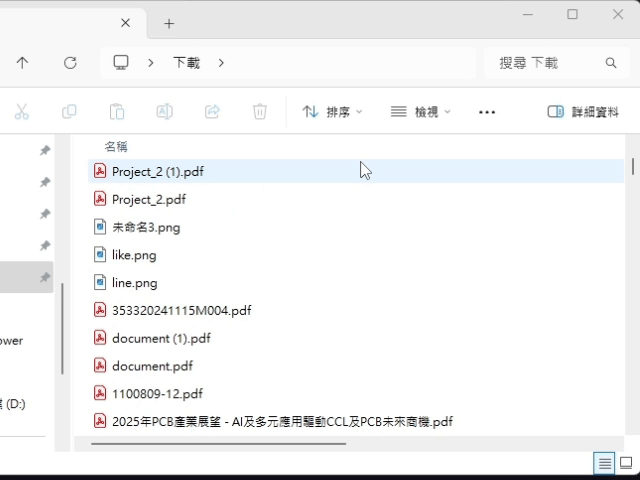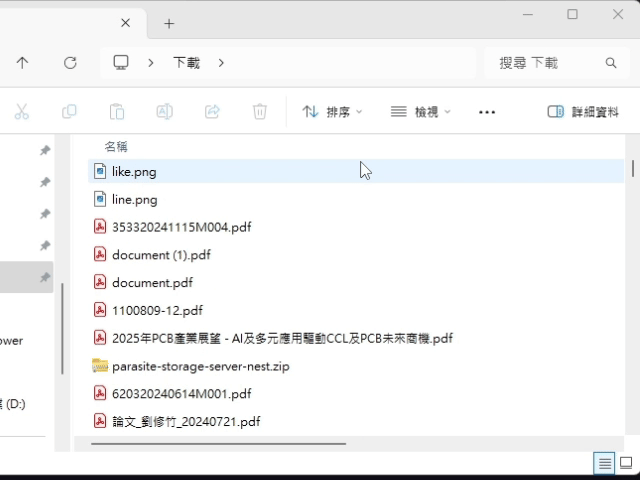
- amount: Amount
set
- set
Horizontal Scroll Percent(percent): Promise<void> Asynchronously invokes the horizontal scrolling action.
(can use HomObject.isScrollable to check UI supports the scroll pattern.)Parameters
- percent: number
Set the percentage of horizontal scrolling.
Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the scroll pattern.
Example
// Before using setHorizontalScrollPercent(), must first update updateCurrentIsScrollable() to confirm whether there is a scroll pattern
const isScrollable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsScrollable()
if (isScrollable) {
await homObject.setHorizontalScrollPercent(50)
}The UI result after calling setHorizontalScrollPercent() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)

- percent: number
set
- set
Value(value): Promise<void> If the UI has value pattern, set the value of the UI.
(can use HomObject.hasValue to check UI supports the value pattern.)Parameters
- value: string
Value used to set the UI.
Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the value pattern.
Remarks
// Before using setValue(), must first update updateCurrentHasValue() to confirm whether there is a value pattern
const hasValue = await homObject.updateCurrentHasValue()
if (hasValue) {
await homObject.setValue('scrollV')
}The UI result after calling setValue() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
- value: string
set
- set
Vertical Scroll Percent(percent): Promise<void> Asynchronously invokes the vertical scrolling action.
(can use HomObject.isScrollable to check UI supports the scroll pattern.)Parameters
- percent: number
Set the percentage of vertical scrolling.
Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the scroll pattern.
Remarks
// Before using setVerticalScrollPercent(), must first update updateCurrentIsScrollable() to confirm whether there is a scroll pattern
const isScrollable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsScrollable()
if (isScrollable) {
await homObject.setVerticalScrollPercent(50)
}The UI result after calling setVerticalScrollPercent() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)

- percent: number
start
- start
Audio Listening(channel?, sampleRate?, bits?): Promise<void> Starts the audio listening.
Parameters
Optionalchannel: numberchannelRate, defaults to 1
OptionalsampleRate: numbersampleRate, defaults to 44100
Optionalbits: numberbits, defaults to 16
Returns Promise<void>
A promise that resolves when the audio listening is started.
Example
// Before using setValue(), must first update updateCurrentHasValue() to confirm whether there is a value pattern
await homObject.startAudioListening()
// or with specific parameters
await homObject.startAudioListening(2)
await homObject.startAudioListening(2, 16000)
await homObject.startAudioListening(2, 16000, 8)
stop
toggle
un
- un
Maximize(): Promise<void> If the UI has window pattern, restore the window.
(Window pattern related functions are not provided yet.)Returns Promise<void>
Throws
UI does not support the window pattern.
Remarks
The UI result after calling unMaximize() is roughly as follows.
(using file explorer as an example)
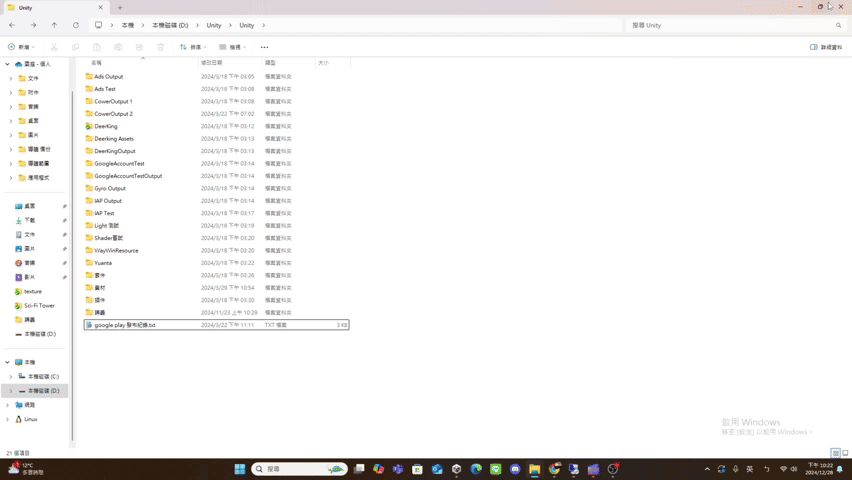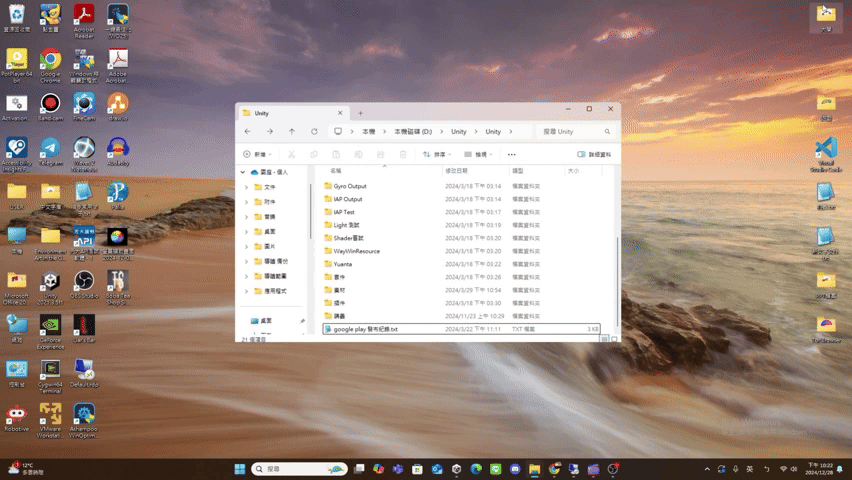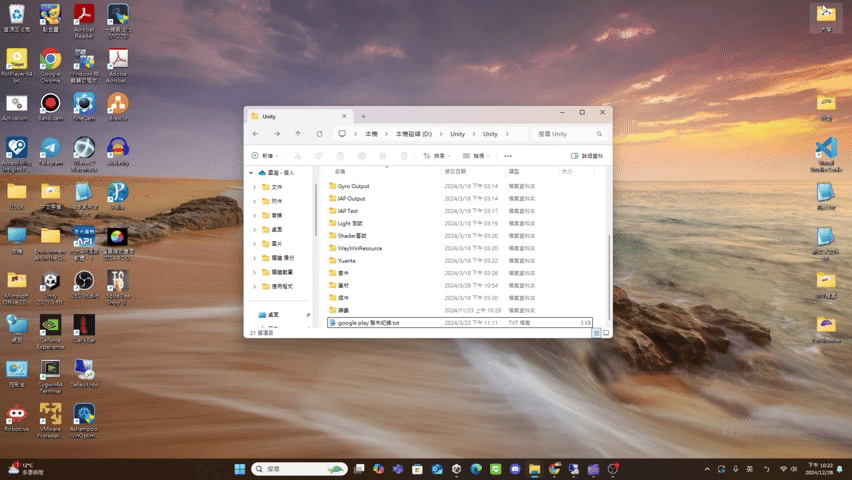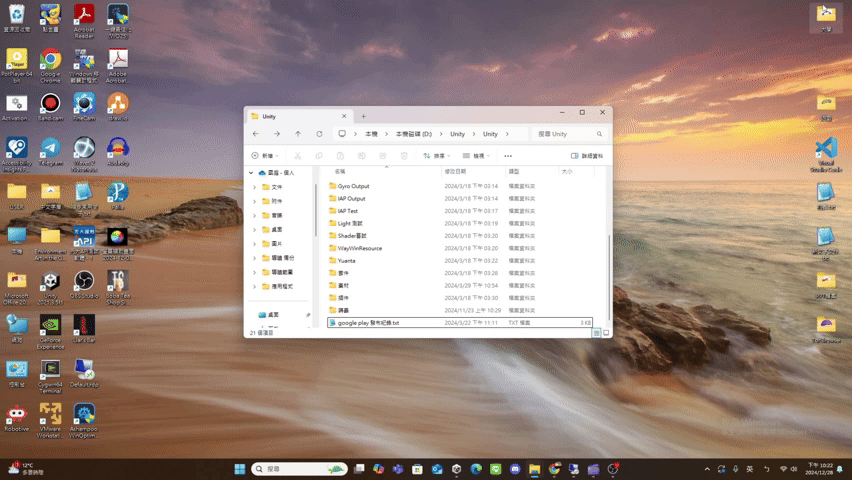
update
- update
Current Bounding Box(): Promise<BoundingBox> Updates the current bounding box property of the UI, this will update HomObject.boundingBox property.
Returns Promise<BoundingBox>
A promise that resolves to the updated bounding box property.
Example
const boundingBox = await homObject.updateCurrentBoundingBox()
// a new homObject.boundingBox property
console.log(boundingBox)
update
- update
Current Has Value(): Promise<boolean> Updates the current hasValue property of the UI, this will update HomObject.hasValue property.
Returns Promise<boolean>
A promise that resolves to the updated hasValue property.
Example
const hasValue = await homObject.updateCurrentHasValue()
// a new homObject.hasValue property
console.log(hasValue)
// homObject.hasValue property can be used to check if the UI has value pattern.
if (hasValue) {
// setValue() only works if the UI has value pattern.
homObject.setValue('new value')
}
update
- update
Current Is Invokable(): Promise<boolean> Updates the current isInvokable property of the UI, this will update HomObject.isInvokable property.
Returns Promise<boolean>
A promise that resolves to the updated isInvokable property.
Example
const isInvokable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsInvokable()
// a new homObject.isInvokable property
console.log(isInvokable)
// homObject.isInvokable property can be used to check if the UI has invoke pattern.
if (isInvokable) {
// invoke() only works if the UI has invoke pattern.
homObject.invoke()
}
update
- update
Current Is Scrollable(): Promise<boolean> Updates the current isScrollable property of the UI, this will update HomObject.isScrollable property.
Returns Promise<boolean>
A promise that resolves to the updated isScrollable property.
Example
const isScrollable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsScrollable()
// a new homObject.isScrollable property
console.log(isScrollable)
// homObject.isScrollable property can be used to check if the UI has scroll pattern.
if (isScrollable) {
// scrollVertical() only works if the UI has scroll pattern.
homObject.scrollVertical(Amount.LargeDecrement)
}
update
- update
Current Name(): Promise<string> Updates the current name property of the UI, this will update HomObject.name property.
Returns Promise<string>
A promise that resolves to the updated name property.
Example
const name = await homObject.updateCurrentName()
// a new homObject.name property
console.log(name)
update
- update
Current Scrollable View(): Promise<ScrollableView> If the UI has scroll pattern, updates the current scrollableView property, otherwise, it will throw an error.
this will update HomObject.scrollableView property.Returns Promise<ScrollableView>
A promise that resolves to the updated scrollableView property.
Remarks
Can use HomObject.isScrollable to check if the UI supports the scroll pattern.
Example
// Before using updateCurrentScrollableView(), must first update updateCurrentIsScrollable() to confirm whether there is a scroll pattern
const isScrollable = await homObject.updateCurrentIsScrollable()
if (isScrollable) {
const scrollableView = await homObject.updateCurrentScrollableView()
// a new homObject.scrollableView property
console.log(scrollableView)
}Throws
UI does not support the scroll pattern.
update
- update
Current Value(): Promise<Value> If the UI has value pattern, updates the current value property, otherwise, it will throw an error.
this will update HomObject.value property.Returns Promise<Value>
A promise that resolves to the updated value property.
Remarks
Can use HomObject.hasValue to check if the UI supports the value pattern.
Example
// Before using updateCurrentValue(), must first update updateCurrentHasValue() to confirm whether there is a value pattern
const hasValue = await homObject.updateCurrentHasValue()
if (hasValue) {
const value = await homObject.updateCurrentValue()
// a new homObject.value property
console.log(value)
}Throws
UI does not support the value pattern.
Abstract base class representing a generic UI object within a Host Object Model (Hom).
This class provides common properties and methods for UI objects within the Hom.